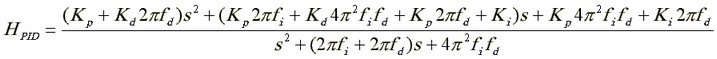The PID Controller consists of an integrator and differentiator with proportional gain.
| • | Gain Kp: The controller gain Kp determines the frequency gain of the controller in the pass band (where integration and differentiation are of no interest). |
| • | Gain Ki: The controller gain Ki determines the shape of the frequency response at low frequencies. |
| • | Gain Kd: The controller gain Kp determines the shape of the frequency response at high frequencies. |
| • | Frequency fi: The integration behavior of the controller starts at frequency fi in Hz. A decrease of this frequency corresponds to a more pure integration behavior. |
| • | Frequency fd: The differentiation behavior of the controller stops at frequency fd in Hz. An increase of this frequency corresponds to a more pure differentiation behavior, reducing the tameness of the controller. |
Transfer function of the controller:
![]()
that equals