Iconic Diagrams\Mechanical\Translation\Transmission
Domains: Continuous. Size: 1-D. Kind: Iconic Diagrams (Translation).
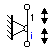
This models represents any type of lever with two counter-moving ports. The lever is ideal, i.e., it does not have inertia, friction or geometrical limitations. The lever has one fast moving port and one slow moving port. The lever ratio is the (absolute) ratio of the velocities of both ports. The causality of this model is always mixed: one port has a force out causality while the other has an velocity out causality:
p_fast.F = -i * p_slow.F
p_slow.v = -i * p_fast.v
or:
p_slow.F = -1/i * p_fast.F
p_fast.v = -1/i * p_slow.v
Ports |
Description |
p_fast p_slow |
Fast moving translation port. Slow moving translation port. |
Causality |
|
p_slow notequal p_fast |
|
Parameters |
|
i |
lever ratio p_slow.v / p_fast.v [], 0 < i < 1 |
Keep the lever ratio i between 0 and 1. Confusion might otherwise exist:
| • | i > 1: the fast moving port is slower than the slow moving port (you better interchange the connections of the lever model). |
| • | i < 0: the ports are not counter-moving (use the transmission model instead). |



