Iconic Diagrams\Mechanical\Translation\Components
Domains: Continuous. Size: 1-D. Kind: Iconic Diagrams (Translation).
C
V
CV
SCVS
LuGre
Domains: Continuous. Size: 1-D. Kind: Iconic Diagrams (Translation).
These models represents friction with the fixed world. The amount of friction depends on the normal force that is applied and the friction function that is used. The normal force is given by the input signal Fn.
![]()
The models have only one initial port p defined. Because any number of connections can be made, successive ports are named p1, p2, p3 etc. 20-sim will automatically create equations such that the resulting force p.F is equal to the sum of the forces of all connected ports p1 .. pn. The velocities of all connected ports are equal to p.v.
p.F = sum(p1.F, p2.F, ....)
p.v = p1.v = p2.v = ....
Due to the use of normal force, the friction models all have a fixed force out causality. The constitutive equations are therefore described as:
p.F = Fn * f(p.v);
with f the friction function.
This model represents friction with the fixed world described as coulomb friction:
p.F = Fn*mu_c*tanh(slope*p.v);
Fn: normal force (given by the input signal Fn)
mu_c: the coulomb friction coefficient
slope: the steepness of the coulomb friction curve.
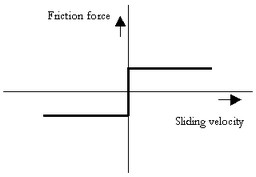
Ports |
Description |
p[any] |
Any number of connections can be made (Translation). |
Causality |
|
Fixed force out |
|
Input |
|
Fn |
Normal force [N] |
Parameters |
|
mu_c slope |
Coulomb friction coefficient [] Steepness of Coulomb friction curve [s/m] |
This model represents friction with the fixed world described as viscous friction:
p.F = Fn*mu_v*p.v;
Fn: normal force (given by the input signal Fn)
mu_v: the viscous friction coefficient
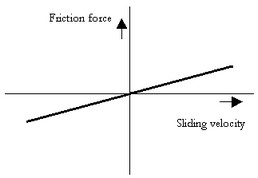
Ports |
Description |
p[any] |
Any number of connections can be made (Translation). |
Causality |
|
Fixed force out |
|
Input |
|
Fn |
Normal force [N] |
Parameters |
|
mu_v |
Viscous friction coefficient [s/m] |
This model represents friction with the fixed world described as coulomb plus viscous friction:
p.F = Fn*(mu_c*tanh(slope*p.v) + mu_v*p.v);
Fn: normal force (given by the input signal Fn)
mu_v: the viscous friction coefficient
mu_c: the coulomb friction coefficient
slope: the steepness of the coulomb friction curve.
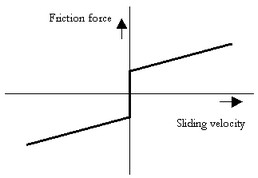
Ports |
Description |
p[any] |
Any number of connections can be made (Translation) |
Causality |
|
Fixed force out |
|
Input |
|
Fn |
Normal force [N] |
Parameters |
|
mu_v mu_c slope |
Viscous friction coefficient [s/m] Coulomb friction coefficient [] Steepness of Coulomb friction curve [s/m] |
This model represents friction with the fixed world described as static plus coulomb plus viscous plus Stribeck friction:
p.F = Fn *
(( mu_c + (mu_st*abs(tanh( slope*p.v )) - mu_c)
* exp( -((p.v / v_st)^2 )) ) * sign(p.v)
+ mu_v * p.v);
Fn: normal force (given by the input signal Fn)
mu_s: the static friction coefficient
mu_v: the viscous friction coefficient
mu_c: the coulomb friction coefficient
slope: the steepness of the coulomb and static friction curve.
v_st: the characteristic Stribeck velocity.
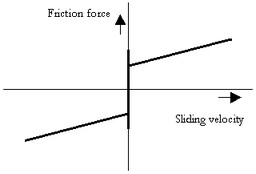
Ports |
Description |
p[any] |
Any number of connections can be made (Translation). |
Causality |
|
Fixed force out |
|
Input |
|
Fn |
Normal force [N] |
Parameters |
|
mu_s mu_v mu_c slope v_st |
Static friction coefficient [] Viscous friction coefficient [s/m] Coulomb friction coefficient [] Steepness of Coulomb friction curve [s/m] Characteristic Stribeck velocity [m/s] |
This model represents friction with the fixed world described by the LuGre friction model:
p.F = FN*f_lg(p.v);
Fn: normal force (given by the input signal Fn)
f_lg: the LuGre friction model
Ports |
Description |
p[any] |
Any number of connections can be made (Translation). |
Causality |
|
Fixed force out |
|
Input |
|
Fn |
Normal force [N] |
Parameters |
|
mu_c mu_s mu_v v_st mu_k |
Coulomb friction coefficient [] Static friction coefficient [] Viscous friction coefficient [s/m] Characteristic Stribeck velocity [m/s] Stiffness coefficient at zero speed [] |