Library
Iconic Diagrams\Mechanical\Translation\Components
Domains: Continuous. Size: 1-D. Kind: Iconic Diagrams (Translation).
This model represents a skyhook damper. It can have an force out as well as an velocity out causality. In the last case the constitutive equation, as shown below, is simply inverted. The model has a fixed force out causality. The equations are:
Force out causality:
p_high.F = d * p_high.v;
p_low.F = p_high.F
As the equations point out, the force of the skyhook damper only depends on the velocity at the port p_high. The position of p_high is indicated by an arrow, as shown in the figure below.
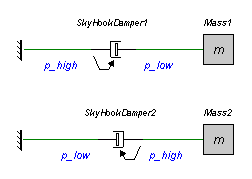
In this figure two models are shown. In the top model, the damping force of the skyhook damper is zero because the velocity at p_high is zero. Consequently the mass is free to move.
In the lower model, the damping force is proportional to the velocity of the mass. Here the skyhook damper acts as a normal damper.
Ports |
Description |
p_high, p_low |
Both Translation ports of the skyhook damper. |
Causality |
|
fixed force out |
|
Parameters |
|
d |
damping [Ns/m] |



