Iconic Diagrams\Hydraulics\Components
Domains: Continuous. Size: 1-D. Kind: Iconic Diagrams (Hydraulics).
When a fluid flow changes speed, a force is needed to accelerate the fluid. This force is equal to the acceleration multiplied by the mass of the fluid.
F = m * dv/dt
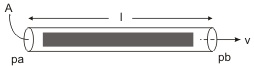
The fluid mass is equal to the pipe area multiplied by the pipe length and the fluid density:
m = A * l * rho
The force will result in a pressure differential:
F = A * dp = A * (pa.p - pb.p)
We can rewrite the formulas as
dp = rho * l * dv/dt
and by introducing the fluid flow phi:
v = phi/A
we get the formula for an hydraulic inertia:
dp = (rho * l / A) * d phi/dt
Ports |
Description |
pa, pb |
Both terminals of the hydraulic inertia. |
Causality |
|
fixed pressure out pa fixed pressure out pb |
|
Parameters |
|
d l |
pipe diameter [m] pipe length [m] |



