Standard PID controller equations operate on the error signal (Error Based):
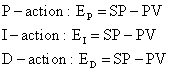
A more flexible structure is obtained by treating the setpoint (SP) and the process output (PV) separately (Setpoint Weighting):
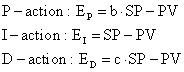
The I-action always operates on the error to insure that the error between setpoint and process output will be minimized.
In most commercial controllers, the parameters b an c are chosen 1 or 0:
b = 1 -> proportional control using the error: SP - PV (error feedback).
b = 0 -> only proportional control on the process output (PV).
c = 1 -> derivative control using the error: SP - PV (error feedback).
c = 0 -> only derivative control on the process output (PV).



