Iconic Diagrams\Hydraulics\Cylinders\Basic Cylinders
Domains: Continuous. Size: 1-D. Kind: Iconic Diagrams (Hydraulics/Translational).
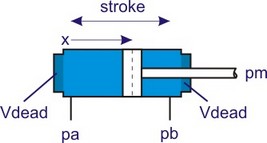
This is an ideal model of cylinder with no mass and no friction. The volume of the chambers is given by:
Va = Vdead + Aa*(x + x_initial)
Vb = Vdead + Ab*(stroke - x - x_initial)
with Aa the piston area and Ab the effective area at the rod side. x is the piston position and Vdead the initial volume when piston position is zero. The piston areas Aa and Ab are related to the piston diameter dp and rod diameter dr by:
Aa = pi * dp^2 / 4
Ab = pi * dp^2 / 4 - pi * dr^2 / 4

There is no restriction on the travel of the piston. Only a warning is given when the maximum stroke is exceeded or the piston position gets negative.
Ports |
Description |
pa, pb pm |
hydraulic port translation port |
Causality |
|
preferred pressure out pa preferred force out pm |
|
Parameters |
|
Vdead stroke x_initial dp dr |
rest volume of oil in cylinder chamber when closed [N.s/m] stroke length [m] starting position of piston [m] piston diameter [m] rod diameter [m] |



