Signal\Block Diagram Non-Linear
Domains: Continuous. Size: 1-D. Kind: Block Diagrams.
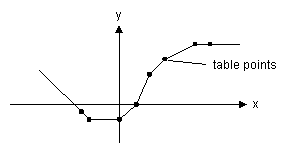
This model uses a one-dimensional table with data points to calculate the output y = f(x) as a function of the input x. The output y is calculated using linear interpolation between the table data points.
| • | The input data of the first column needs to be monotonically increasing. |
| • | Discontinuities are allowed, by providing the same input point twice in the table. |
| • | Values outside of the table range, are computed by linear extrapolation of the last two points. |
table
-2.5 -2 0 1 2 3 5 6 |
-0.5 -1 -1 0 2 3.0 4 4.0 |
|
A table must be stored either as an ASCII (text) file or as a matrix inside the equation model. In both cases the table should consist two columns of data. The first column consists of the x-values and the second column of the corresponding y-values.
If the table is read from a file, each line of the file may only contain one x- and one corresponding y-value. The two values must be separated by a space or a tab. Each new set of x- and y-values must start on a new line. No comment or other text may be part of the table-file. The filename of the input file can be specified using the complete path (e.g. C:\data\data.tbl). When no path is given, the file is assumed to be in the experiment directory.
Inputs |
Description |
input |
|
Outputs |
|
output |
|
Parameters |
|
filename |
The filename of the table file. |
If the table is read from a matrix in an equation model, each row may only contain one x- and one corresponding y-value. The two values must be separated by a coma and each column must be separated by a semi-colon.
Table interpolation can also be used directly in an equation model by using the function table.