y = table(file_name,x);
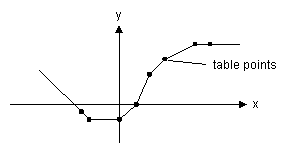
This model uses a one-dimensional table with data points to calculate the output y = f(x) as a function of the input x. The output y is calculated using linear interpolation between the table data points.
| • | The input data x of the first column needs to be monotonically increasing. |
| • | Discontinuities are allowed, by providing the same input point twice in the table. |
| • | Values outside of the table range, are computed by linear extrapolation of the last two points. |
The first argument (file_name) of this function must be a parameter of the type string and is used as a reference to a filename. This reference can be specified using the complete path or relative to the model directory. The second argument (x) should be a real variable.
table
-2.5 -2 0 1 2 3 5 6 |
(example):
-0.5 -1 -1 0 2 3.0 4 4.0 |
|
A table must be stored as an ASCII (text) file or a Comma Separated Values (.csv) file and should consist two columns of data. The first column consists of the x-values and the second column of the corresponding y-values. Each line of the file may only contain one x- and one corresponding y-value. The two values must be separated by a space or a tab. Each new set of x- and y-values must start on a new line. No comment or other text may be part of the table-file.
parameters
string filename = 'data.txt';
variables
real y;
real x;
equations
x = ramp(1);
y = table(filename,x);
Example data.txt format:
-2.5, -0.5
-2.0, -1.0
0.0, -1.0
1.0, 0.0
2.0, 2.0
3.0, 3.0
5.0, 4.0
6.0, 4.0
x and y must be scalars. from_file must be string parameter.